Epilepsy
What is Epilepsy?
Epilepsy is a chronic neurological disorder characterized by recurrent seizures, which are sudden, temporary disturbances in brain function. Seizures can affect anyone, regardless of age, sex, or background.
Brain Changes During Epilepsy
1. Electrical Discharges: Abnormal electrical activity in brain cells (neurons) leads to excessive firing, causing seizures.
2. Neuronal Synchronization: Normal brain activity is synchronized; in epilepsy, this synchronization is disrupted.
3. Neurotransmitter Imbalance: Imbalance of neurotransmitters (e.g., glutamate, GABA) contributes to seizure activity.
4. Blood Flow Changes: Altered blood flow to affected brain areas.
Types of Epilepsy
1. Idiopathic Epilepsy: No known cause.
2. Symptomatic Epilepsy: Caused by brain injury, infection, or genetics.
3. Cryptogenic Epilepsy: Unknown cause, possibly genetic.
Types of Seizures
1. Generalized Tonic-Clonic (GTC) Seizures: Convulsions, loss of consciousness.
2. Partial Seizures: Localized symptoms, e.g., arm twitching.
3. Absence Seizures: Brief loss of consciousness, staring.
4. Myoclonic Seizures: Sudden muscle jerks.
Causes and Risk Factors
1. Genetics
2. Head trauma
3. Brain infections (meningitis, encephalitis)
4. Stroke
5. Brain tumors
6. Birth defects
Symptoms
1. Seizures
2. Confusion
3. Memory loss
4. Mood changes
5. Fatigue
Diagnosis
1. Medical history
2. Physical examination
3. Electroencephalogram (EEG)
4. Imaging tests (MRI, CT scans)
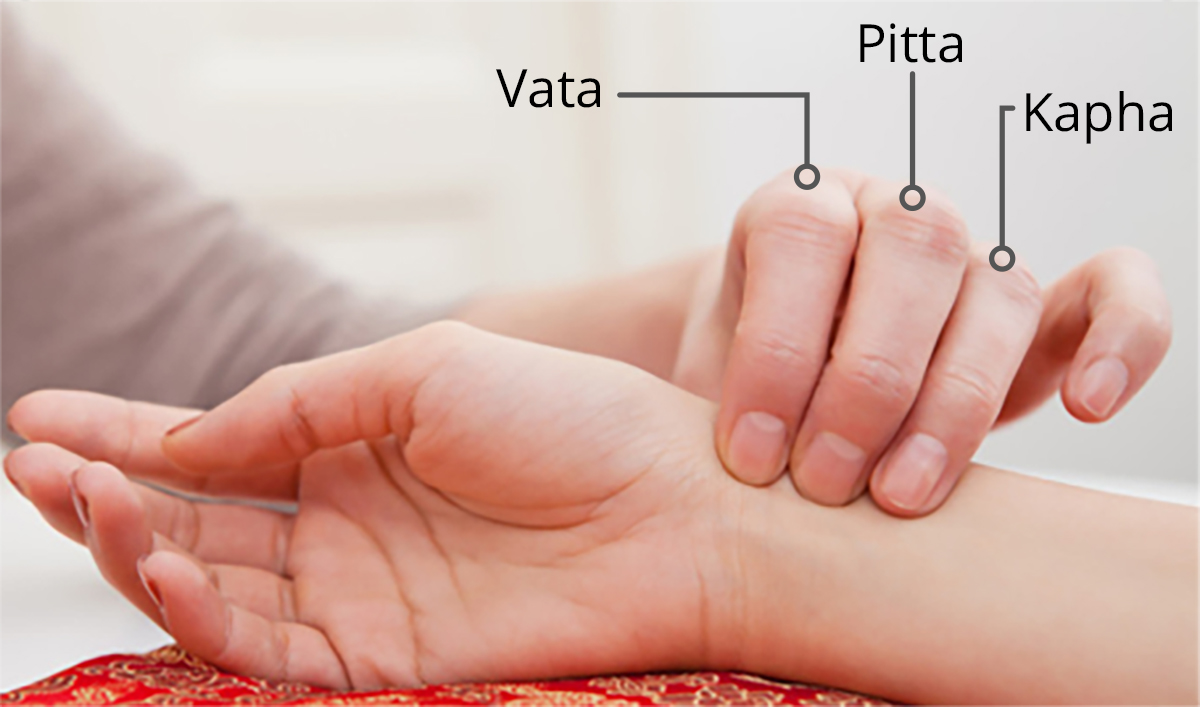
Ayurveda treatment for Epilepsy
In Ayurveda, Epilepsy is considered a "Vata" disorder, caused by:
1. Imbalanced Vata dosha
2. Poor digestion
3. Toxic accumulation (ama)
4. Stress and anxiety
Treatment Principles
1. Balance Vata dosha through diet, lifestyle, and herbs
2. Reduce stress and anxiety with yoga and meditation
3. Enhance cognitive function with rasayana herbs
4. Detoxify with Panchakarma procedures
Herbal Remedies
1. Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera): Anti-stress, anti-anxiety
2. Brahmi (Bacopa monnieri): Enhances cognitive function
3. Turmeric (Curcuma longa): Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant
4. Ginger (Zingiber officinale): Digestive, anti-inflammatory
5. Guggulu (Commiphora mukul): Detoxifying, anti-inflammatory
Ayurvedic Formulations
1. Kaishore Guggulu: Anti-inflammatory, detoxifying
2. Maha Yogaraj Guggulu: Nourishing, rejuvenating
3. Triphala: Digestive, detoxifying
Panchakarma Procedures
1. Abhyangam: Warm oil massage for relaxation
2. Shirodhara: Oil pouring on forehead for calmness
3. Njavarakizhi: Rice pouch therapy for joint nourishment
4. Basti: Medicated enema for detoxification
Dietary Recommendations
1. Warm, nourishing foods (rice, lentils, vegetables)
2. Avoid cold, dry foods (raw vegetables, salads)
3. Include ghee, oil, and spices (turmeric, cumin)
4. Drink lukewarm water, herbal teas
Lifestyle Changes
1. Regular exercise (yoga, walking)
2. Stress management (meditation, deep breathing)
3. Sleep hygiene (consistent sleep schedule)
4. Avoid excessive physical strain
Treatment Duration
Treatment duration varies depending on severity and individual response. Typically, 3-6 months of intensive treatment, followed by maintenance therapy.







.jpg)