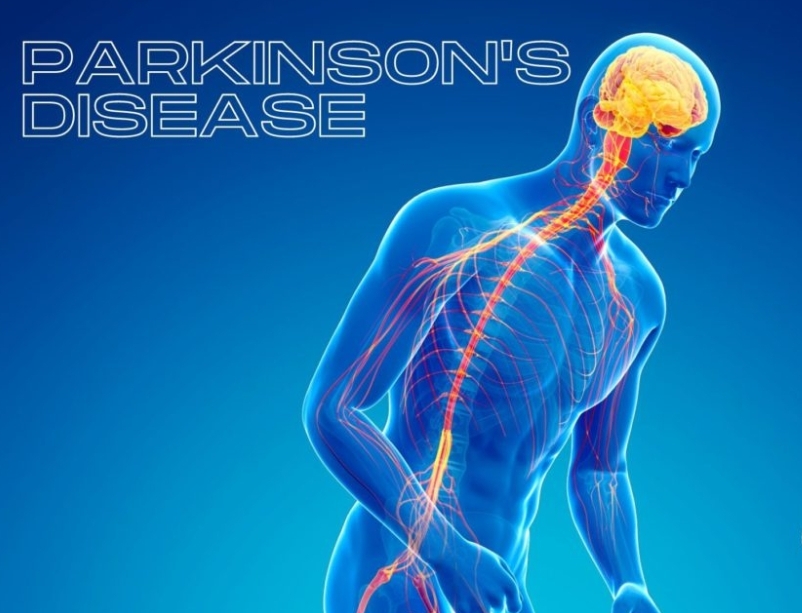
Parkinsons Disease
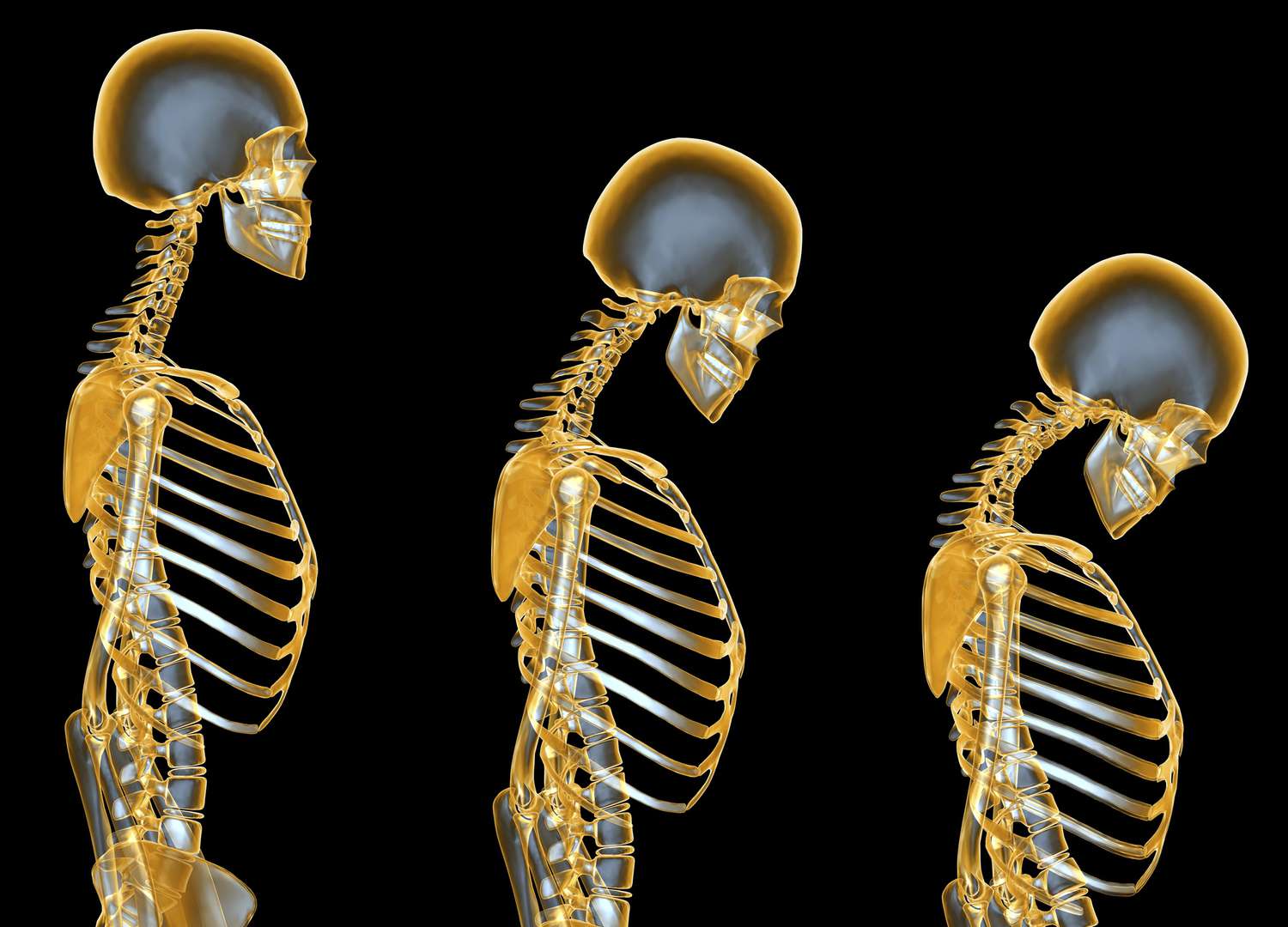
Parkinson's disease (PD) is a progressive neurological disorder affecting movement, balance, and coordination. It results from the degeneration of dopamine-producing neurons in the brain, leading to tremors, rigidity, and difficulty with movement.
Gut-Brain Connection:
Recent research highlights the gut's role in PD:
1. Gut microbiome imbalance (dysbiosis): Altered gut bacteria composition.
2. Gut inflammation: Increased inflammation in the gut and brain.
3. Gut-brain axis: Bidirectional communication between gut and brain via vagus nerve.
4. Gut-derived neurotoxins: Production of neurotoxic compounds in the gut.
Key Findings:
1. Gut bacteria produce dopamine and other neurotransmitters.
2. Gut inflammation increases alpha-synuclein (a protein linked to PD).
3. Antibiotics use is associated with increased PD risk.
4. Fecal microbiota transplantation (FMT) shows promise in PD models.
Symptoms of PD
Early symptoms:
1. Tremors (hands, fingers, or chin)
2. Rigidity (stiffness)
3. Bradykinesia (slow movement)
4. Postural instability (balance problems)
Advanced symptoms:
1. Difficulty walking
2. Freezing (sudden inability to move)
3. Dystonia (involuntary muscle contractions)
4. Cognitive impairment
5. Mood changes (depression, anxiety)
Stages
1. Early stage: Mild symptoms, minimal impact on daily life.
2. Moderate stage: Noticeable symptoms, some difficulty with daily activities.
3. Advanced stage: Significant symptoms, substantial impact on daily life.
Causes and Risk Factors
1. Genetics
2. Environmental toxins (pesticides, heavy metals)
3. Age (risk increases after 60)
4. Family history
5. Head injuries
Diagnosis
1. Medical history
2. Physical examination
3. Neurological tests (e.g., tremor analysis)
4. Imaging tests (e.g., MRI, CT scans)
Treatment { As Per Modern Medicine}
1. Medications (dopamine replacement, MAO-B inhibitors)
2. Deep brain stimulation (DBS)
3. Physical therapy
4. Occupational therapy
5. Lifestyle changes (exercise, stress management)
Ayurveda Treatment for Parkinsons Disease
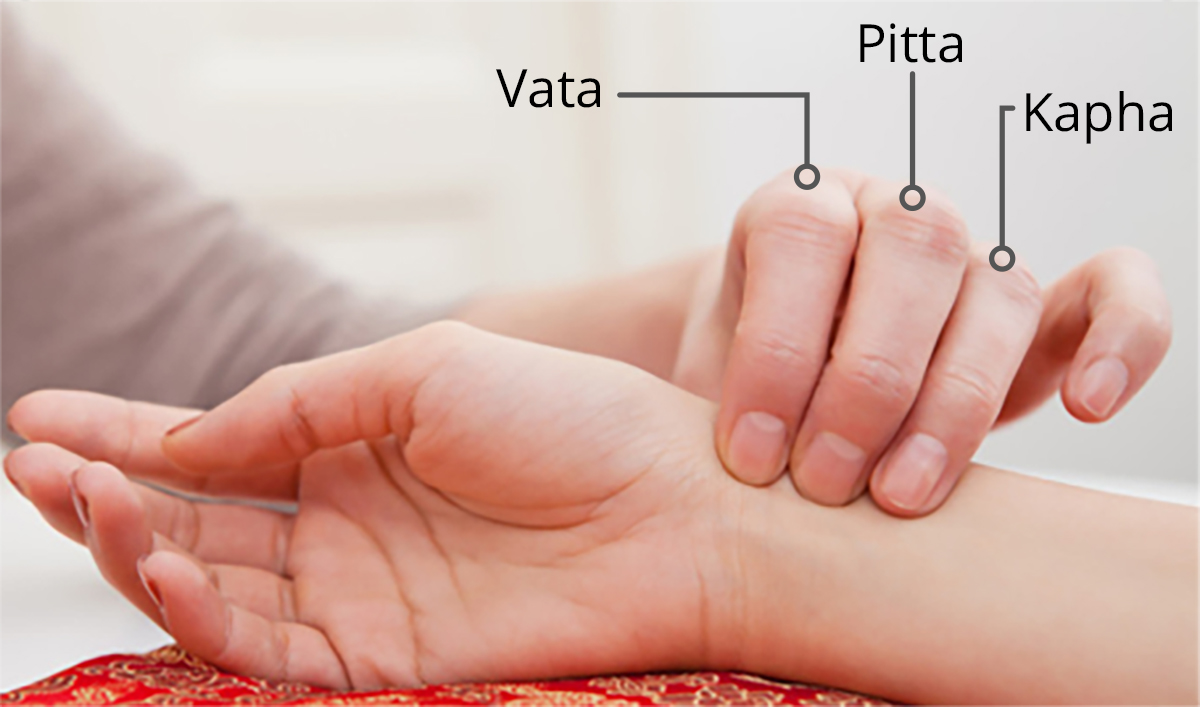
In Ayurveda, Parkinson's disease is considered a "Vata" disorder, characterized by an imbalance of the Vata dosha. This imbalance affects the nervous system, leading to tremors, rigidity, and movement difficulties..At Gayatri's Heritage Ayurveda the intensity of vata disorder is identified by Nadi Pariksha and specific internal and external treatments are advised to balance it out and cure the disease.
Treatment Principles
1. Balance Vata dosha through diet, lifestyle, and herbs.
2. Nourish brain tissue (Medha) with rasayana herbs.
3. Enhance dopamine levels with herbal supplements.
4. Reduce stress and anxiety with yoga and meditation.
Herbal Remedies
The following are some of the main herbal ingridients used in preparation of medicines for PD at Gayatri,s heritage Ayurveda
1. Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera): Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant.
2. Brahmi (Bacopa monnieri): Enhances cognitive function, memory.
3. Turmeric (Curcuma longa): Anti-inflammatory, antioxidant.
4. Ginger (Zingiber officinale): Digestive, anti-inflammatory.
5. Guggulu (Commiphora mukul): Detoxifying, anti-inflammatory.
Ayurvedic Formulations
1. Kaishore Guggulu: Anti-inflammatory, detoxifying.
2. Maha Yogaraj Guggulu: Nourishing, rejuvenating.
3. Triphala: Digestive, detoxifying.
Panchakarma Procedures
1. Abhyangam: Warm oil massage for relaxation.
2. Shirodhara: Oil pouring on forehead for calmness.
3. Njavarakizhi: Rice pouch therapy for joint nourishment.
4. Basti: Medicated enema for detoxification.
Dietary Recommendations
1. Warm, nourishing foods (rice, lentils, vegetables).
2. Avoid cold, dry foods (raw vegetables, salads).
3. Include ghee, oil, and spices (turmeric, cumin).
4. Drink lukewarm water, herbal teas.
Lifestyle Changes
1. Regular exercise (yoga, walking).
2. Stress management (meditation, deep breathing).
3. Sleep hygiene (consistent sleep schedule).
4. Avoid excessive physical strain.
Treatment Duration
Treatment duration varies depending on severity and individual response. Typically 21-28 days External tPanchakarma reatments and, 3-6 months of internal medications, followed by maintenance therapy.







.jpg)