Neuropathy
What is Neuropathy ?
Neuropathy, mostly referring to peripheral neuropathy, is a condition caused by damage or disease affecting the nerves outside the brain and spinal cord. This damage disrupts the signals between the central nervous system and the rest of the body, leading to various symptoms that usually begin in the hands or feet .
Symptoms
Symptoms depend on which type of nerves are affected (sensory, motor, or autonomic) and can range from mild to severe.
- Sensory nerve symptoms (most common):
- Numbness, prickling, or tingling, often described as "pins and needles".
- Burning, sharp, stabbing, or electric shock-like pain.
- Extreme sensitivity to touch, where even bed sheets can be painful (allodynia).
- Reduced ability to feel pain, temperature changes, or vibration, increasing the risk of unnoticed injuries.
- Loss of balance or coordination.
- Motor nerve symptoms:
- Muscle weakness, cramps, or twitching.
- Loss of muscle control and mass.
- Difficulty with complex movements, such as buttoning a shirt or walking (foot drop).
- Autonomic nerve symptoms:
- Problems with digestion (constipation, diarrhea, feeling full quickly).
- Bladder control issues or difficulty emptying the bladder.
- Sudden drops in blood pressure when standing up, causing dizziness or fainting.
- Abnormal sweating (too much or too little).
- Sexual dysfunction, such as erectile dysfunction.
Causes of Neuropathy
Neuropathy has many causes, including:
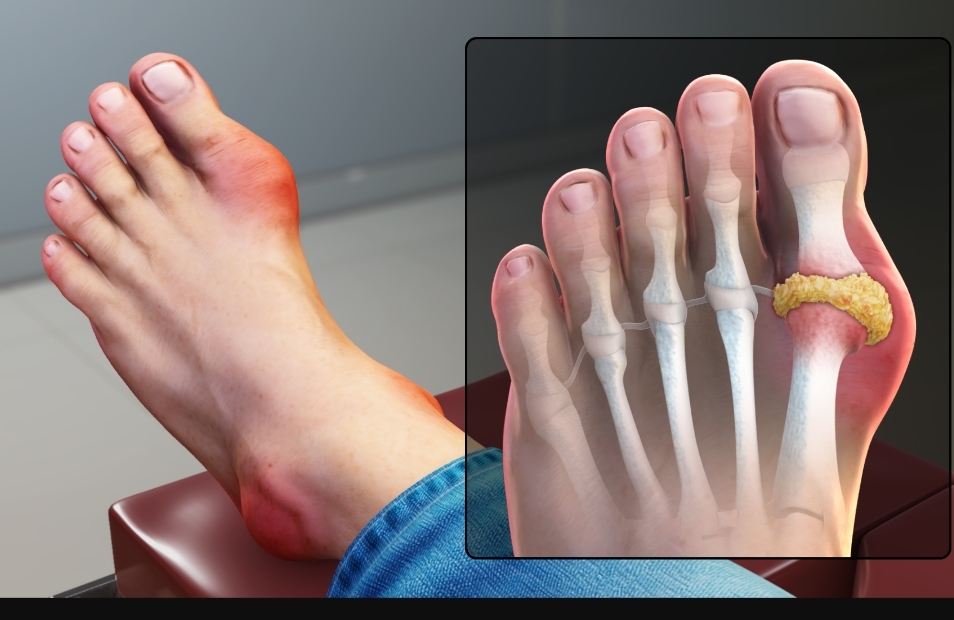
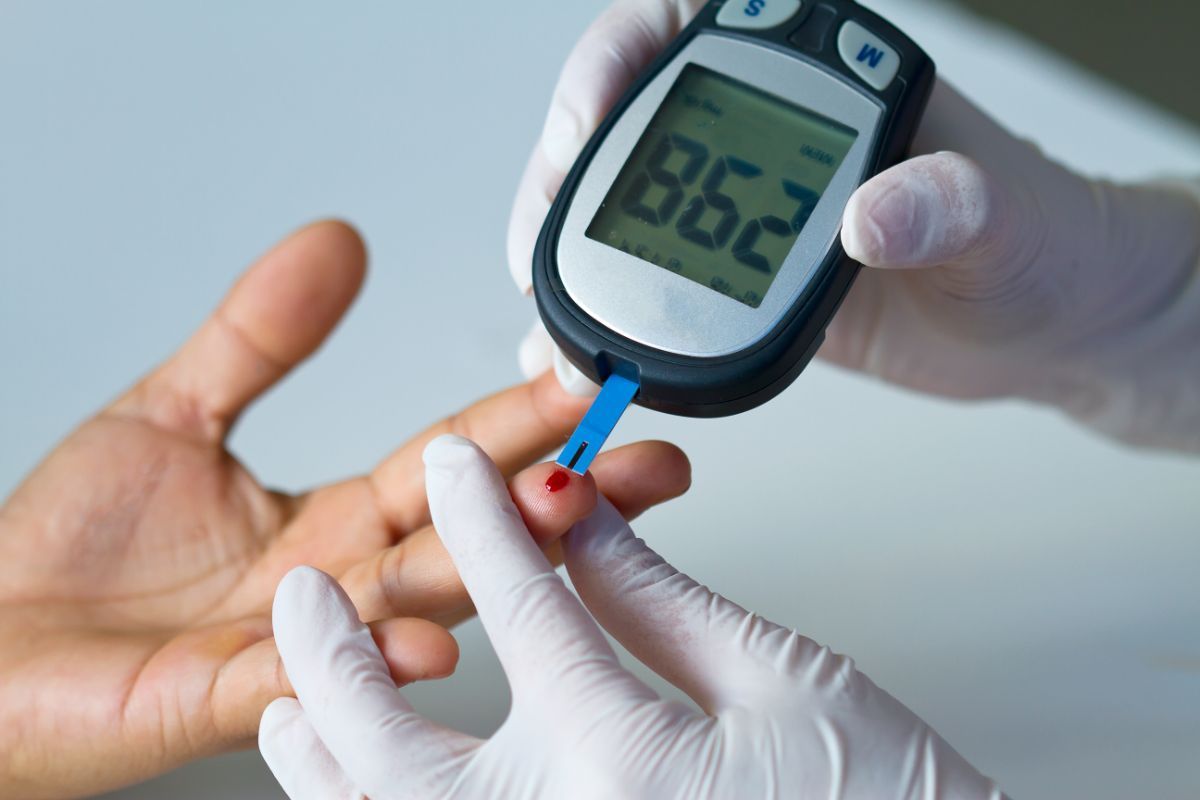
- Diseases: Diabetes (the most common cause), autoimmune disorders (lupus, rheumatoid arthritis, Guillain-Barré syndrome), kidney or liver disease, and certain infections like shingles, HIV, or Lyme disease.
- Physical injury: Trauma, pressure on a nerve (such as in carpal tunnel syndrome), or sustained cold exposure.
- Toxins and medications: Long-term, heavy alcohol use, chemotherapy drugs, and exposure to industrial chemicals or heavy metals.
- Nutritional deficiencies: Low levels of vitamins B1, B6, B12, or E.
- Inherited conditions: Genetic disorders like Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease.
- Idiopathic: In many cases, no cause can be identified.
Diagnosis and Treatment as per Modern medicine
Diagnosis in neuropathy through a medical history, physical and neurological exams, and various tests, which may include blood tests, nerve function tests (EMG and nerve conduction studies), and imaging tests.
Treatment focuses on managing the underlying cause and alleviating symptoms.
- Treating the cause: Managing blood sugar levels for diabetes, correcting vitamin deficiencies, avoiding alcohol, or using immunosuppressant drugs for autoimmune conditions can help slow progression or even reverse symptoms in some cases.
- Symptom management:
- Medications, including certain anti-seizure drugs (gabapentin, pregabalin) and antidepressants (duloxetine, amitriptyline), are often used for nerve pain.
- Physical therapy can help with muscle weakness and balance issues.
- Lifestyle adjustments such as a healthy diet, regular exercise, and daily foot checks (especially for people with diabetes) are crucial for prevention and management.
- Devices like braces, canes, or special footwear may improve mobility and prevent injury.
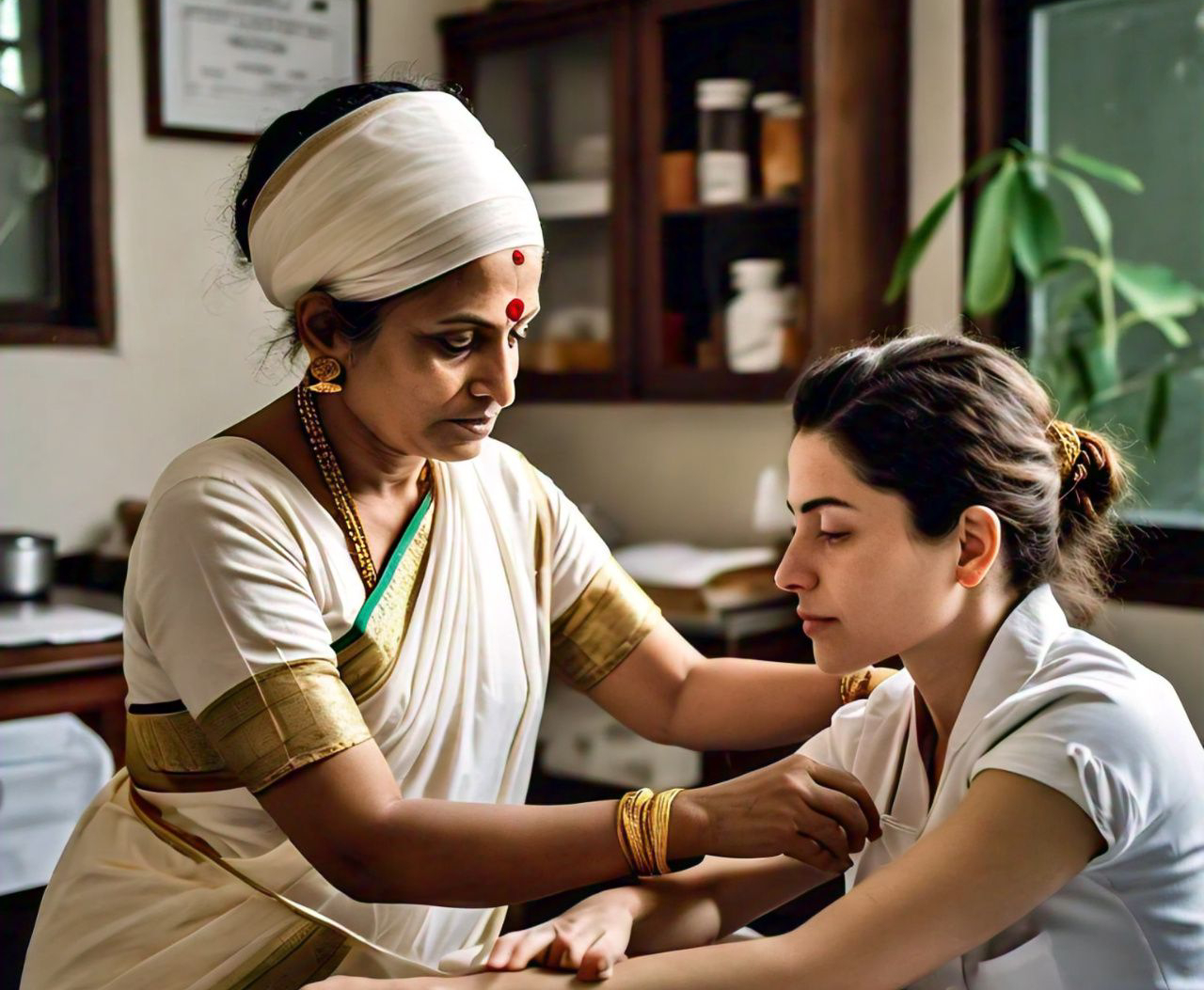
Ayurveda Treatment for Neuropathy
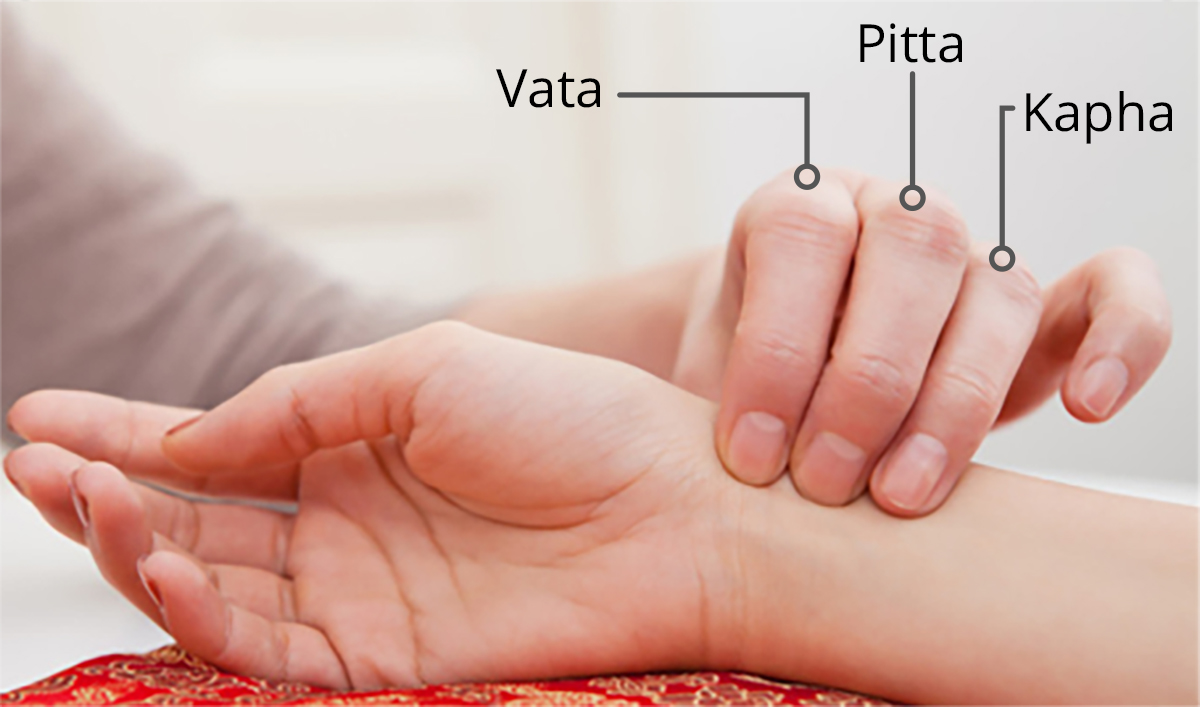
At Gayatri's Heritage Ayurveda we offer a holistic approach to neuropathy, primarily by balancing the Vata dosha, which governs the nervous system, and removing toxins (ama). Treatment focuses on personalized care involving specialized therapies, herbal remedies, and dietary and lifestyle adjustments, often in conjunction with conventional medical advice. These treatments are advised on a case by case basis after subjecting to patient to Nadi Pariksha [ Ayurvedic Pulse Diagnosis] to find out the actuals levels of imbalance in basic constituents of Vata,Pitha and Kapha
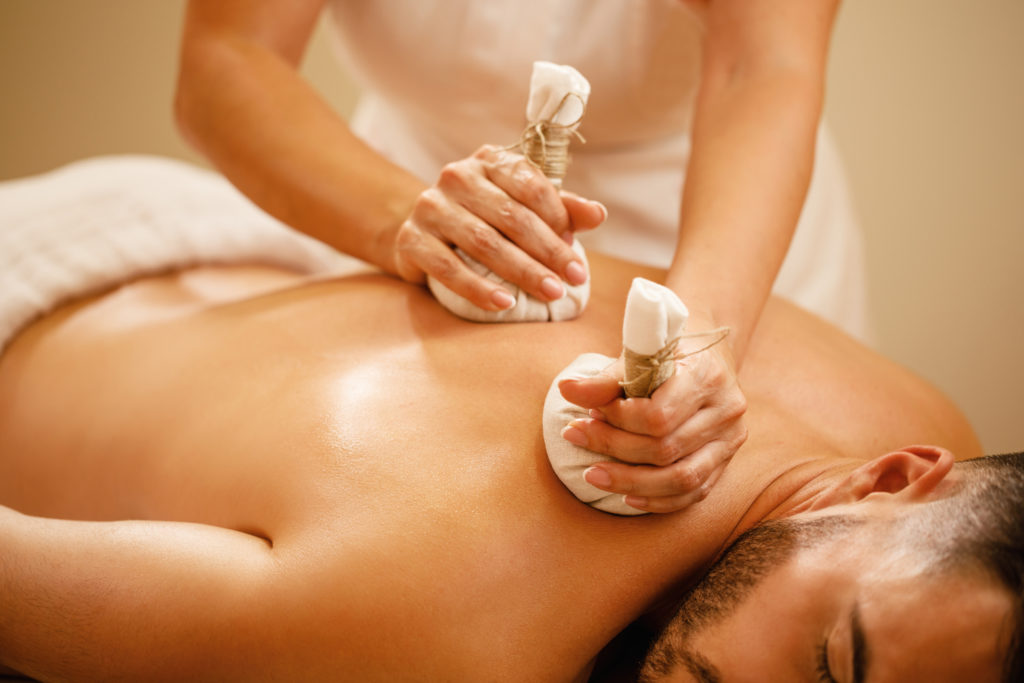
Ayurvedic Therapies (Panchakarma)
For chronic and complicated cases, detoxification and rejuvenation therapies, collectively known as Panchakarma, are often recommended under expert supervision.
- Abhyanga (Oil Massage): Full-body massage with warm medicated oils (like Ksheerabala or Mahanarayana taila) helps improve circulation, nourish nerve tissues, and reduce pain and stiffness.
- Vasti (Medicated Enema): Considered highly effective for Vata disorders, Basti involves administering medicated oils or herbal decoctions through the rectum to cleanse toxins and balance Vata.
- Swedana (Sudation/Steam Therapy): Gentle steam therapy helps loosen toxins, reduce stiffness, and improve blood flow.
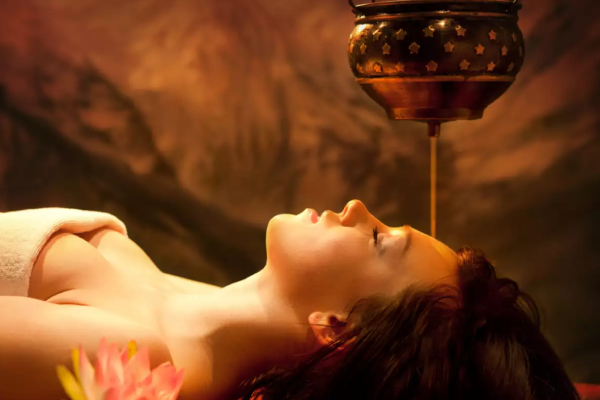
- Shirodhara: A continuous stream of warm herbal oil is poured over the forehead to calm the nervous system, relieve mental stress, and manage symptoms like tingling and numbness.
- Pizhichil: A therapeutic oil bath where warm, medicated oil is continuously poured over the body to soothe nerves and relax muscles.
- Nasya: Administration of medicated oils or herbal powders through the nasal passages to treat conditions affecting the upper body and improve nerve function.
Herbal Remedies: Internal Medications
At Gayatri we have internal medicines made out of mainly the following specific herbs known for their neuroprotective and anti-inflammatory properties for treatment of Neuropathy.
- Ashwagandha (Withania somnifera): A potent adaptogen that helps reduce stress, inflammation, and supports nerve regeneration.
- Brahmi (Bacopa monnieri): Known for enhancing nerve health, improving cognitive function, and possessing neuroprotective properties.
- Turmeric (Curcuma longa): Contains curcumin, a strong anti-inflammatory compound that reduces nerve inflammation and pain.
- Guduchi (Tinospora cordifolia): An immune-boosting herb with anti-inflammatory and antioxidant properties that help in detoxifying the body.
- Bala (Sida cordifolia): Used to strengthen nerves and muscles and reduce neuropathic pain.
Diet and Lifestyle Adjustments
Lifestyle modifications are a crucial part of the treatment to support nerve health and prevent further damage.
- Vata-Balancing Diet: Consuming warm, cooked, oily, and grounding foods (like soups, stews, ghee, and whole grains) is recommended. Bitter-tasting vegetables may help regulate blood sugar in cases of diabetic neuropathy.
- Foods to Avoid: Limit cold, raw, fried, processed, and sugary foods, as well as excessive caffeine and alcohol, which can aggravate Vata dosha.
- Physical Activity: Gentle exercises such as walking, swimming, and yoga can improve blood circulation to the nerves and manage stress.
- Stress Management: Practices like meditation and pranayama (breathing exercises) help calm the nervous system
HBOT for Neuropathy
At Gayatri's Heritage Ayurveda we have option to combine HBOT [ Hyberbaric oxygen Therapy] along with ayurveda as a catalyst to increase the bio availibilty of medicines used in treatment. The cells become more 'alive' due to increased oxygen levels ,prompting faster healing and increasing the effectiveness of ayurveda treatments.
How HBOT Works for Neuropathy
- Increases Oxygen Levels: Patients breathe 100% oxygen in a pressurized chamber, dramatically increasing oxygen in blood plasma, which reaches deep tissues and damaged nerves.
- Promotes Nerve Repair: Increased oxygen supports nerve regeneration, blood vessel formation (angiogenesis), and stem cell activity, helping to heal damaged peripheral nerves.
- Reduces Inflammation: HBOT has anti-inflammatory effects, reducing swelling and protecting nerve cells from damage (neuroprotection).
- Improves Circulation: It helps restore microcirculation, vital for nerve health, especially in diabetic neuropathy.
Potential Benefits
- Pain Relief: Alleviates neuropathic pain and symptoms like tingling and numbness.
- Functional Improvement: Can improve nerve conduction velocity (NCV), an objective measure of nerve function, and motor function.
- Wound Healing: Particularly helpful for nerve-related wounds and diabetic foot ulcers by improving blood flow.







.jpg)